
Wolf: The Marvellous Predator of the Wilderness
Wolf: The Marvellous Predator of the Wilderness
Introduction
The wolf, revered and feared across cultures, stands as one of the most iconic and misunderstood predators in the animal kingdom. Known for its strength, intelligence, and complex social structures, this apex predator plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Found across North America, Europe, and Asia, wolves are adaptable creatures that have captured human imagination for centuries. This article delves into the fascinating world of wolves, exploring their habitats, physical characteristics, behaviors, and much more.
Amazing Facts
Wolves are extraordinary animals with numerous intriguing attributes:
- Social Structure: They live in highly organized packs, usually consisting of an alpha pair, their offspring, and other related or unrelated wolves. This social structure helps them coordinate hunting and care for the young.
- Communication: These animals are highly vocal and use a variety of sounds, including howls, barks, growls, and whines, to communicate within the pack.
- Territory: Packs maintain territories ranging from 50 to over 1,000 square miles, which they mark and defend vigorously.
- Diet: As carnivores, their diet primarily consists of large ungulates such as deer, elk, and moose, but they also consume smaller mammals, birds, and even fish.
- Speed and Endurance: They can run at speeds up to 40 miles per hour (64 km/h) and travel long distances, sometimes covering over 30 miles (48 km) in a day.
Habitat and Food
Wolves are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, reflecting their resilience and versatility.
Habitat:
- Found in diverse habitats, including forests, tundras, deserts, and grasslands.
- They are commonly seen in North America, Europe, and Asia, though their range has diminished due to human activity.
- These predators prefer areas with sufficient prey and minimal human disturbance, often occupying remote and rugged terrains.
Food:
- Primarily carnivorous, they hunt large ungulates such as Deer, Elk, Moose, and Bison.
- Their diet also includes smaller mammals, birds, and fish. They scavenge when necessary, feeding on carrion left by other predators.
- Wolves hunt in packs, using coordinated strategies to take down prey much larger than themselves. This cooperative hunting is essential for their survival, particularly in harsh environments.
Appearance
Wolves are known for their striking and powerful appearance. Key characteristics include:
- Size: They vary in size depending on the region, with adults weighing between 60 to 175 pounds (27 to 80 kg) and standing 26 to 32 inches (66 to 81 cm) tall at the shoulder.
- Color: Their fur color ranges from white, gray, brown, to black, often with a mix of these colors, providing effective camouflage in different environments.
- Build: These animals have long legs, large paws, and muscular bodies designed for endurance and strength.
- Face: They have a broad head, erect ears, and keen, amber-colored eyes that convey intelligence and alertness.
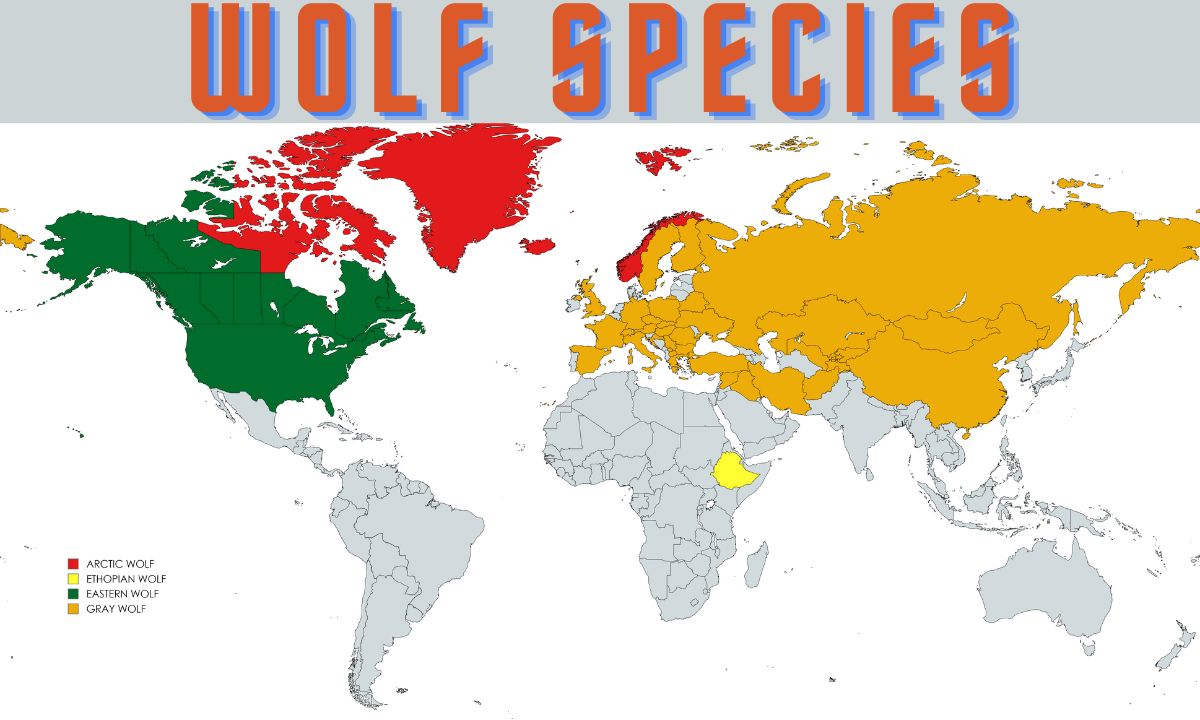
Types/Subspecies of Wolves
There are several species and subspecies, each with unique traits and adaptations to their specific environments:
- Gray Wolf (Canis lupus):
- The most widespread and well-known species, found across North America, Europe, and Asia. This species includes numerous subspecies, such as the Arctic wolf, timber wolf, and Mexican wolf.
- Ethiopian Wolf (Canis simensis):
- Native to the Ethiopian Highlands, this species is characterized by its reddish coat and specialized diet of rodents.
- Red Wolf (Canis rufus):
- Found in the southeastern United States, this critically endangered species has a distinctive reddish-brown coat and is smaller than the gray wolf.
- Eastern Wolf (Canis lycaon):
- Inhabits the Great Lakes region and southeastern Canada, often considered a distinct species or a subspecies of the gray wolf.
Predators and Threats
Despite being apex predators, wolves face various natural and human-induced threats that impact their survival.
Natural Predators:
- Other Large Carnivores: Occasionally, Bears and Tigers can prey on young or injured individuals, though such incidents are rare.
- Disease: Wolves are susceptible to diseases such as rabies, canine distemper, and parvovirus, which can significantly affect populations.
Threats:
- Habitat Loss: Urban development, agriculture, and deforestation reduce available habitats, leading to conflicts with humans.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: They often come into conflict with humans when they prey on livestock, leading to retaliatory killings.
- Hunting and Trapping: In some areas, wolves are hunted or trapped for their fur or to control their population.
- Climate Change: Alterations in weather patterns and habitat conditions due to climate change can impact prey availability and habitat suitability.
Mating
These animals exhibit unique and complex mating behaviors, essential for the continuation of their species.
- Breeding Season: Typically occurs once a year, usually from January to March.
- Courtship: Alpha pairs engage in courtship behaviors such as grooming, vocalizations, and physical displays of affection.
- Gestation and Birth: After a gestation period of about 63 days, the female gives birth to a litter of 4 to 6 pups in a den, which provides a safe environment for the young.
- Parental Care: Both parents and other pack members help raise the pups, providing food, protection, and teaching essential survival skills. Pups are weaned at about 8 to 10 weeks old and begin hunting with the pack by 6 months.
How They Communicate
Wolves use various methods to communicate with each other, particularly during hunting and social interactions.
Vocalizations:
- Howls: Used to communicate over long distances, often to assemble the pack, mark territory, or signal alarm.
- Barks and Growls: Used during close-range interactions to express aggression, submission, or playfulness.
- Whines and Whimpers: Often used between pups and adults to communicate needs or submission.
Body Language:
- Posturing: Wolves use body postures, such as raised hackles, tail positioning, and ear movements, to convey dominance, submission, or readiness to mate.
- Facial Expressions: Expressions such as bared teeth, flattened ears, and narrowed eyes communicate intentions and emotions.
Chemical Signals:
- Scent Marking: They use scent glands and urine to mark territory, signal reproductive status, and communicate with other pack members.
Religious and Cultural Significance
Wolves hold significant symbolic and cultural importance in various societies:
Indigenous Cultures:
- Spiritual Symbol: Many Native American tribes view them as symbols of strength, loyalty, and wisdom, often featuring prominently in myths, legends, and ceremonies.
- Totem Animals: In some cultures, they are considered totem animals, embodying the traits and virtues of the people or clans they represent.
Modern Symbolism:
- Conservation Icon: Wolves are often used in conservation campaigns to raise awareness about wildlife protection and the importance of preserving natural habitats.
- Popular Culture: These animals appear in various forms of media, from literature and art to movies and television, symbolizing wildness, freedom, and the untamed spirit of nature.
Movies Featuring These Iconic Predators
Wolves have been the central focus of numerous feature films, documentaries, and nature films, showcasing their behaviors and the challenges they face:
- “Dances with Wolves” (1990): A film that explores the relationship between a Civil War soldier and a wolf, highlighting themes of companionship and understanding.
- “The Grey” (2011): A survival thriller featuring a pack of wolves as central figures, emphasizing their role as apex predators in the wilderness.
- “Never Cry Wolf” (1983): A film based on Farley Mowat’s autobiographical book, portraying the author’s experiences studying wolves in the Arctic.
- “Wolves” (2016): A documentary that delves into the lives and struggles of these animals, showcasing their importance in maintaining ecological balance.
Pronunciation in Different Languages
The term for these iconic predators is pronounced differently across various languages, reflecting linguistic diversity:
- English: /wʊlf/
- Spanish: /lobo/
- French: /loup/
- German: /Wolf/
- Italian: /lupo/
- Mandarin Chinese: /狼 (láng)/
- Japanese: /狼 (ōkami)/
- Russian: /волк (volk)/
- Arabic: /ذئب (thiʾb)/
- Hindi: /भेड़िया (bhēṛiyā)/
FAQs
Q: What do wolves eat? A: They are primarily carnivores, hunting large ungulates such as deer, elk, moose, and bison. Their diet also includes smaller mammals, birds, and fish, and they scavenge when necessary.
Q: Where do wolves live? A: Wolves inhabit diverse habitats, including forests, tundras, deserts, and grasslands, found across North America, Europe, and Asia. They prefer areas with sufficient prey and minimal human disturbance.
Q: How do wolves communicate? A: They communicate through vocalizations such as howls, barks, and growls, body language including posturing and facial expressions, and chemical signals like scent marking.
Q: Are wolves endangered? A: While some populations are stable, others face threats from habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, hunting, and disease. Conservation efforts are essential to protect their populations.
Q: What is unique about wolf reproduction? A: Wolves typically form monogamous pairs, with both parents and other pack members helping to raise the pups. After a gestation period of about 63 days, the female gives birth to a litter of 4 to 6 pups in a den.
The wolf symbolizes the beauty and resilience of the wild, playing a vital role in its ecosystem and human culture. This exploration highlights their unique traits and behaviors, celebrating the complexity and charm of these remarkable predators.
This Article is Sponsored by FINCTOP & TECHETOP










