American Crocodile: Guardian of the Coastal Wetlands

The American Crocodile: Guardian of the Coastal Wetlands
The American crocodile, Crocodylus acutus, stands as a testament to the resilience and complexity of coastal ecosystems in the Americas. Misunderstood by many, this reptilian predator embodies the untamed essence of its habitat, navigating a delicate balance between survival and the increasing pressures of human encroachment. This exploration into the life of the American Crocodile aims to demystify the creature, shedding light on its ecological importance, the challenges it faces, and the concerted efforts required to ensure its continued place in the natural world.
The American Crocodile: An Overview
Physical Characteristics
The American Crocodile is distinguished by its striking appearance, featuring a narrow, V-shaped snout and a robust body that can reach lengths of up to 16 feet in mature adults. This physical design is not merely for show; it enables the crocodile to exert impressive bite force, crucial for capturing prey. The crocodile’s armor, composed of tough, bony plates called osteoderms, provides protection against predators and abrasive environments alike.
Distribution and Habitat
With a range that extends from the southern tip of Florida, throughout the Caribbean islands, and down into the northern regions of South America, the American Crocodile is a versatile inhabitant of both freshwater and brackish environments. This species thrives in mangrove swamps and coastal estuaries and occasionally ventures into saltwater, showcasing an impressive adaptability to varying salinity levels that few other crocodiles can manage.
Habitat and Adaptations
Preferred Habitats
The American Crocodile’s preference for warm, tropical climates leads it to inhabit areas where water and land intersect. Mangroves and estuaries provide not only the ideal conditions for hunting and nesting but also crucial camouflage against threats. Such habitats are vital for the crocodile’s lifecycle, offering a sanctuary for vulnerable hatchlings and juveniles.
Adaptations to Salinity and Freshwater
One of the American Crocodile’s most remarkable adaptations is its ability to regulate salt intake, allowing it to thrive in environments with varying salinity. This physiological trait is facilitated by specialized glands in their tongue, which expel excess salt, enabling them to consume saltwater prey and drink saline water without dehydration—a key adaptation for survival in coastal ecosystems.
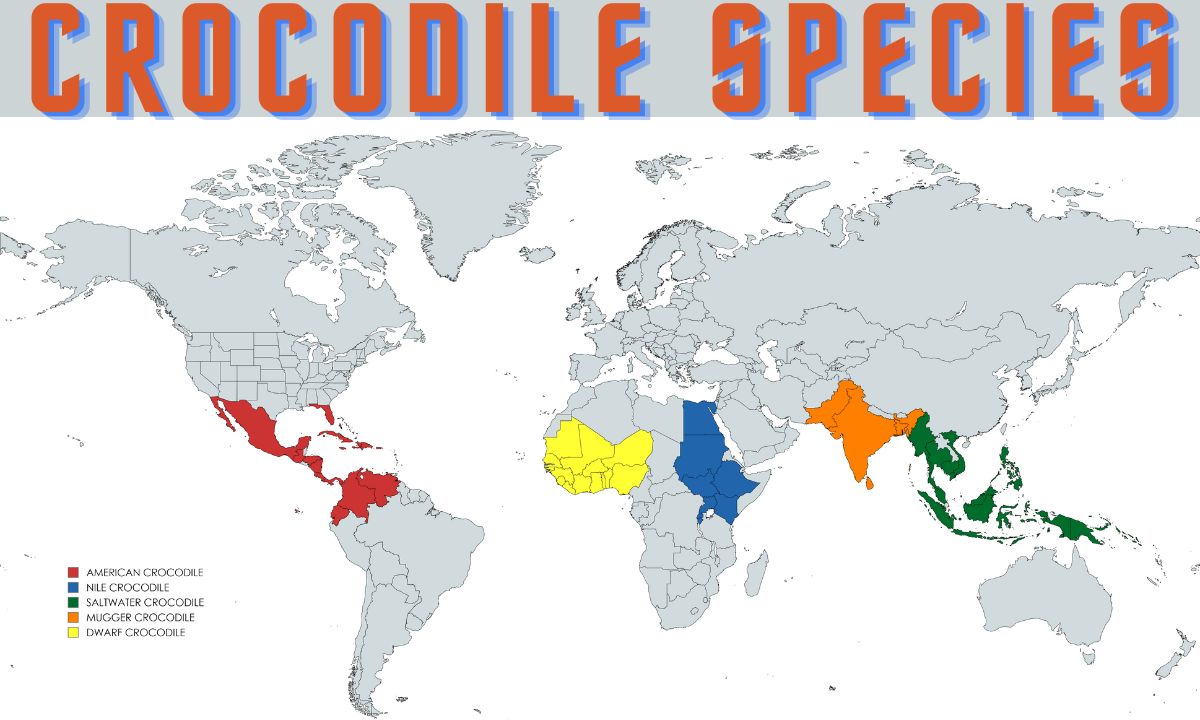
Dwarf Crocodile Nile Crocodile Mugger Crocodile Saltwater Crocodile
Diet and Hunting Strategies
What the American Crocodile Eats
The diet of the American crocodile is as diverse as the ecosystems it inhabits, ranging from fish and crustaceans to small mammals and occasionally birds. This varied diet helps control the populations of certain species, ensuring a balanced ecosystem. The crocodile’s role as an apex predator is vital in maintaining the health of its habitat, preventing any single species from overwhelming the ecological equilibrium.
Hunting Techniques
Masters of ambush, American crocodiles utilize their aquatic environment to stealthily approach prey before launching a swift attack. Their powerful tails enable quick bursts of speed, while their webbed feet allow for silent, undetectable movement in the water. This hunting prowess underscores the crocodile’s role in the food web, acting as a regulator for species populations and contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem.
Reproductive Behavior and Lifecycle
Mating Rituals
The reproductive season of the American crocodile is a time of heightened activity and competition. Males display aggressive behaviors to assert dominance and attract mates, including loud bellowing and a display of physical strength. Females, in turn, select mates based on these displays, ensuring that only the strongest genes are passed on to the next generation.
Nesting and Hatchling Care
After mating, female crocodiles meticulously construct nests on riverbanks or sandy shores, where they lay their eggs. The temperature of the nest, determined by its construction and the warmth of the environment, will determine the sex of the hatchlings. Mothers guard their nests fiercely, demonstrating a maternal instinct that ensures the highest possible survival rate for their offspring in a world filled with predators.
Conservation Status
Threats to Survival
The American Crocodile faces numerous threats, primarily habitat destruction due to coastal development, pollution, and illegal hunting. These challenges are compounded by climate change, which affects nesting sites and food availability. The survival of this species is indicative of the health of its ecosystems, making its preservation a priority for conservationists.
Conservation Efforts and Successes
Conservation efforts for the American Crocodile have seen significant successes, thanks to legal protection, habitat restoration, and public education programs. Protected areas and wildlife reserves have been established to safeguard key habitats, while research into crocodile behavior and ecology informs ongoing conservation strategies. These efforts not only benefit the American crocodile but also countless other species that share its habitat.
Human and Crocodile Interactions
Historical Context
Historically, the American crocodile has been viewed with a mixture of awe and fear, leading to conflicts with human populations. Overhunting for their hide and habitat encroachment significantly reduced their numbers. However, changing perceptions and increased awareness of their ecological role have led to improved coexistence strategies.
Current Challenges and Solutions
As human populations expand into crocodile habitats, encounters between the two are more frequent, necessitating innovative solutions to prevent conflict. Educational programs aimed at local communities, alongside the construction of crocodile-proof barriers and the promotion of crocodile-friendly fishing practices, have proven effective in reducing negative interactions, paving the way for a more harmonious coexistence.
The American Crocodile in Culture and Mythology
Symbolism and Significance
The American Crocodile holds a significant place in the mythology and cultural heritage of the indigenous peoples of the Americas, symbolizing strength, creation, and guardianship. This reverence is a reminder of the deep connections between humans and nature and the importance of respecting and preserving our natural world.
Representation in Media and Folklore
From fearsome beasts to wise guardians, the portrayal of American crocodiles in media and folklore reflects the complex relationship between humans and these ancient creatures. By challenging negative stereotypes and highlighting their ecological importance, contemporary representations can play a crucial role in conservation efforts.
Understanding Crocodile Behavior
Social Structure
Contrary to the solitary image often associated with crocodiles, American crocodiles exhibit complex social behaviors, including a hierarchical structure influenced by size and age. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for managing crocodile populations and ensuring their successful cohabitation with human communities.
Territorial Behaviors
Territorial disputes among American crocodiles, particularly during mating season, are a spectacle of dominance and power. These behaviors, while potentially dangerous, are a natural part of their lifecycle and crucial for the selection of strong mates, ensuring the health and vitality of future generations.
The Role of the American Crocodile in Ecosystems
Ecosystem Impact
As apex predators, American crocodiles play a critical role in their ecosystems, regulating species populations and contributing to the health of their environments. Their presence is a marker of ecological balance, indicating the overall health of coastal and freshwater ecosystems.
Importance as a Keystone Species
The American crocodile’s influence extends beyond its immediate surroundings, affecting a wide range of species and habitats. Protecting the crocodile is synonymous with protecting an entire ecosystem, highlighting the interconnectedness of all living things and the importance of conservation efforts.
American Crocodile
Unique Features and Interesting Facts
From their ancient lineage to their remarkable adaptations to aquatic life, American crocodiles are a living link to a distant past. These creatures are not only survivors of millennia but also integral components of their ecosystems, deserving of our respect and protection.
Future Prospects
Ongoing Research
Research into the American crocodile’s behavior, genetics, and habitat needs continues to provide valuable insights for conservation strategies. By understanding more about these creatures, we can better protect them and ensure their survival for generations to come.
The Importance of Habitat Conservation
The preservation of American crocodile habitats is essential for their survival and the well-being of countless other species. Efforts to protect and restore these environments are crucial, requiring the commitment of governments, conservation organizations, and local communities alike.
Conclusion
The American crocodile serves as a powerful symbol of the wild’s resilience and the delicate balance of our ecosystems. Through conservation, research, and responsible coexistence, we can ensure that this ancient predator continues to thrive, maintaining the health and diversity of its habitats. The story of the American crocodile is a reminder of our interconnectedness with nature and the responsibility we bear to protect our planet’s incredible biodiversity.
Author is a passionate writer with an engineering background, driven by a deep love for animals. Despite a successful entrepreneurial career, Saad's true passion lies in sharing his knowledge and insights about animals with the world.
Panda Bear: Gentle Giants of China’s Bamboo Forests
June 13, 2024
Leave a reply Cancel reply
More News
-
Mongoose: Nature’s Intrepid Snake Hunter
June 3, 2024 -
Muntjac: Small and Ancient Deer of the Forest
June 11, 2024 -
Barasingha: Swamp Deer of India
June 11, 2024





