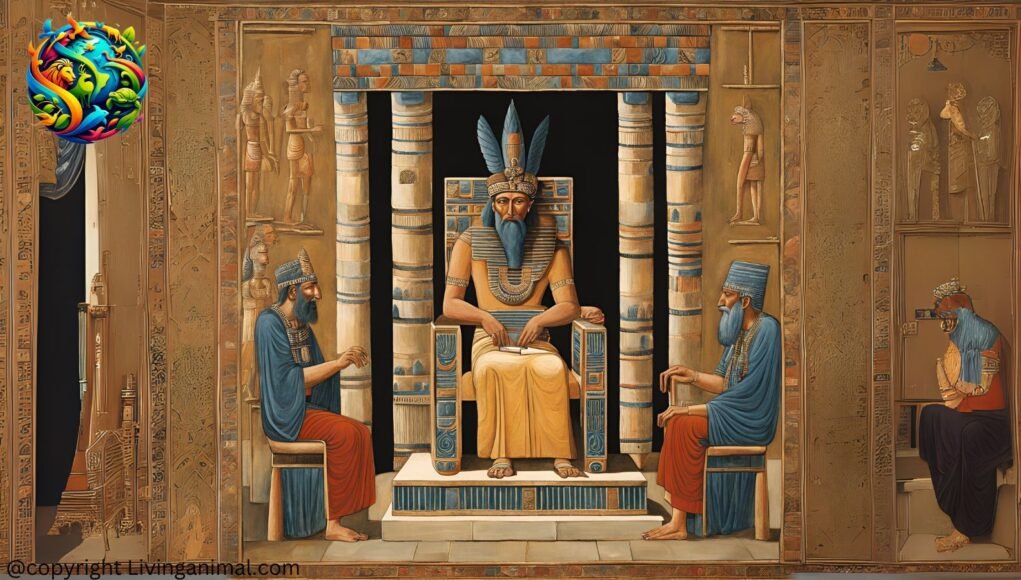
Introduction
The dawn of human civilization saw the rise of many great societies, and among the earliest known was an advanced culture that flourished in Mesopotamia. Sumerian civilization is widely regarded as one of the first urban civilizations in human history. Emerging around 4500 BCE in modern-day Iraq, it laid the foundation for writing, architecture, governance, and many other societal advancements that shaped the course of human history.
Founder of the Sumerian Civilization
The exact founder of this civilization remains unknown, as it was a gradual development rather than the creation of a single individual. However, historical records indicate that early city-states such as Uruk, Ur, and Eridu played a significant role in its formation. A legendary ruler, Enmerkar of Uruk, is often credited in mythology as one of the key figures in its development. The region was home to independent city-states, each governed by a king or priest-king who ruled under divine authority.
Amazing Facts about Sumerian Civilization
- They developed one of the first writing systems, known as cuneiform, around 3100 BCE.
- Their legal codes predate the famous Code of Hammurabi.
- They invented the wheel, revolutionizing transportation and agriculture.
- Their city of Uruk is often considered the world’s first true city.
- They practiced advanced mathematics, using a base-60 system still evident in modern timekeeping.
- They worshipped a pantheon of gods, including Anu (sky god) and Enlil (wind god).
- Their architectural innovations included the ziggurat, a massive step-like temple structure.
- They were pioneers in irrigation, enabling them to cultivate arid lands.
- The Epic of Gilgamesh, one of the oldest known literary works, originated in their culture.
- They brewed beer, one of the earliest recorded alcoholic beverages.
Appearance

Artifacts and sculptures suggest that the people of this civilization had distinctive physical features. They are often depicted with long, curly hair and beards, particularly among men of higher status. Both men and women wore garments made from wool or flax, with elite individuals donning more elaborate and colorful clothing. Jewelry, including rings and necklaces, was common among both genders. Women often wore long robes, while men preferred skirts or tunics. Facial grooming was important, as evident from the elaborate beards shown in their artwork.
How Sumerian Civilization Communicated (Sumerian Tablets)
Communication in this civilization was primarily through the cuneiform script, which was inscribed on clay tablets using a reed stylus. This writing system was initially pictographic but evolved into a complex set of wedge-shaped symbols. It was used for record-keeping, legal documents, religious texts, and literature. Additionally, spoken language played a significant role, and scholars believe they spoke a now-extinct language that was unrelated to any known linguistic family. Their communication also extended to artistic expression, with detailed carvings and tatues conveying religious and political messages.

A composite copy of a text listing cities from the late Uruk period, such as Nippur, Uruk, Ur, Eresh, Kesh, and Zabala.
Movies on the Sumerian Civilization
While Hollywood has often focused on Egyptian and Greco-Roman cultures, some films and documentaries have touched on the rich history of this ancient civilization. Some notable ones include:
- The Epic of Gilgamesh (animated adaptations and short films based on the ancient text)
- The Sumerians (documentary-style productions covering history and contributions)
- Ancient Civilizations (a series exploring early cultures, including this one)
Although mainstream cinema has yet to produce a blockbuster film centered solely on this civilization, it has been referenced in various historical and mythological contexts in popular media.
Sumerian Civilization Known Geographic Location
The civilization occupied a region that corresponds to modern-day southern Iraq, particularly around the cities of Uruk, Ur, Lagash, Nippur, and Eridu. The map below illustrates the extent of their known settlements:
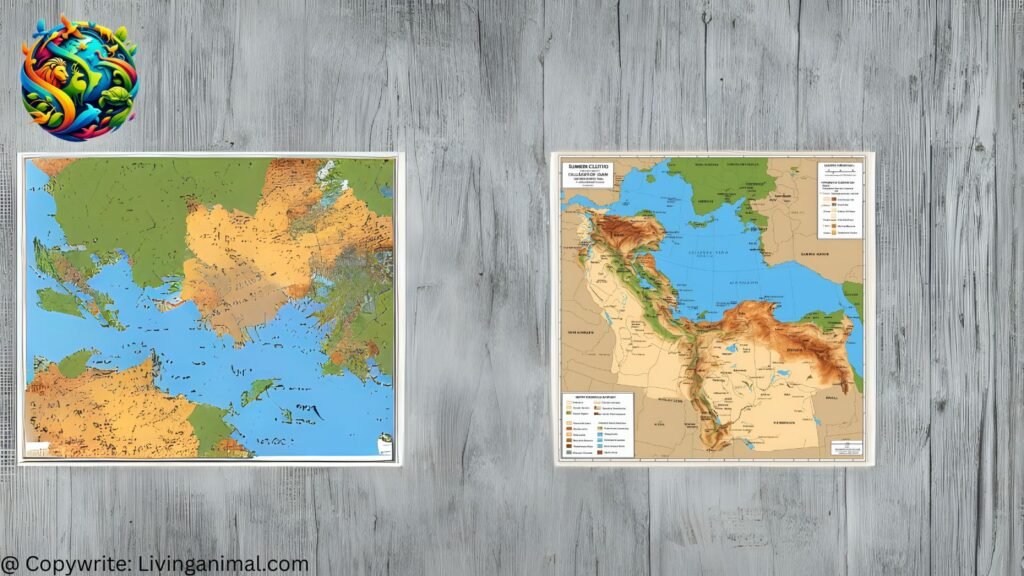
This area was characterized by marshlands, riverbanks, and arid plains, making irrigation essential for agriculture. Despite environmental challenges, they managed to create a prosperous and influential culture that spread its influence beyond Mesopotamia.
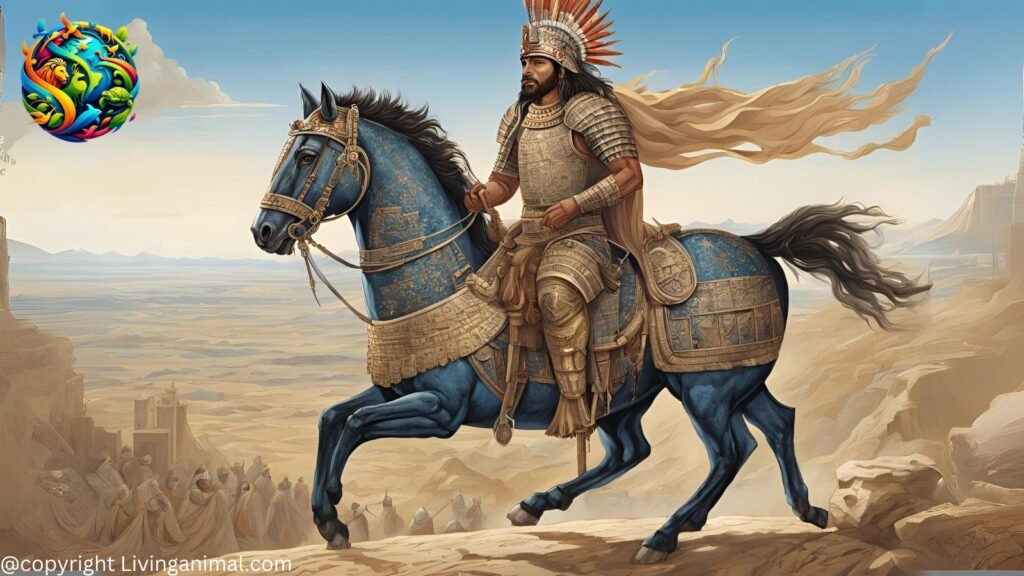
Sumerian Warriors
Warfare played a crucial role in sumerian civilization, as city-states often engaged in conflicts over resources and territory. Their warriors were typically equipped with spears, bows, and early forms of bronze weaponry. They used chariots drawn by donkeys in battle, an innovation that later influenced military tactics in other cultures. Soldiers wore leather or metal armor, and their helmets were designed for protection in close combat. The ruling class often maintained standing
armies to defend their city-states and expand their influence. The famous Stele of the Vultures, a carved stone monument, depicts one of the earliest known representations of organized warfare.

Here are 10 cool facts about the Sumerian civilization:
- First Writing System: They developed cuneiform, one of the earliest known writing systems, around 3100 BCE. It was originally pictographic but later evolved into wedge-shaped symbols.
- World’s First Cities: The Sumerians built some of the first true cities, including Uruk, Ur, and Eridu. Uruk is often considered the world’s first large city, housing tens of thousands of people.
- Inventors of the Wheel: They are credited with inventing the wheel, which revolutionized transportation, pottery-making, and warfare.
- Advanced Mathematics: They used a base-60 numerical system, which influenced modern timekeeping (60 seconds in a minute, 60 minutes in an hour) and geometry.
- First Known Legal Codes: Before Hammurabi’s Code, the Sumerians had legal systems like the Code of Ur-Nammu, which established laws and punishments.
- Epic of Gilgamesh: The world’s oldest recorded literary work, The Epic of Gilgamesh, originated in Sumer. It tells the story of King Gilgamesh and his adventures, including a flood story similar to Noah’s Ark.
- Ziggurat Temples: Their massive step-pyramids, called ziggurats, served as religious centers and were dedicated to their gods. The most famous is the Ziggurat of Ur.
- Beer Brewing Pioneers: The Sumerians were among the first to brew beer, and they even had a goddess of brewing, Ninkasi. Beer was a staple in their diet and used as currency.
- Sophisticated Irrigation: They developed advanced irrigation techniques to control the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, enabling them to cultivate crops in the arid Mesopotamian environment.
- First Schools: The Sumerians established some of the earliest known schools, where scribes were trained in writing and record-keeping, ensuring their civilization’s knowledge was passed down.
FAQs about the Civilization
- What was their greatest contribution to human history?
- Their development of cuneiform writing was one of the most significant contributions, paving the way for recorded history and written communication.
- What language did they speak?
- They spoke a language that is not related to any known linguistic family. It remains a linguistic isolate.
- Did they have a structured government?
- Yes, their city-states were ruled by priest-kings who had both religious and political authority.
- What religion did they follow?
- They practiced polytheism, worshipping gods such as Anu, Enlil, and Inanna.
- How did Sumerian Civilization influence later civilizations?
- Their innovations in writing, law, mathematics, and governance influenced the Babylonians, Assyrians, and other Mesopotamian cultures.
- What led to their decline?
- A combination of factors, including invasions from the Akkadians and environmental changes, contributed to their decline.
- Did Sumerian Civilization invent the wheel?
- Yes, they are credited with inventing the wheel, which had a significant impact on transportation and agriculture.
- How advanced was their medicine?
- They practiced early forms of medicine, including herbal remedies and surgical procedures.
- What type of art did they create?
- They produced intricate sculptures, cylinder seals, and detailed carvings that depicted religious and daily life scenes.
- Are there any surviving structures from sumerian civilization?
- Yes, remnants of ziggurats and city ruins still exist, providing valuable insights into their architectural achievements.




